Kubernetes 101 - Architecture
In this Kubernetes 101 series, we will walk through what is Kubernetes and its architecture. The next article will cover the basis of the Kubernetes objects and concepts.
- Part 1: Kubernetes 101 - Architecture (this article)
- Part 2: Kubernetes 101 - Objects
What is Kubernetes ?
Kubernetes, also known as kube or k8s, is portable, extensible, open-source container orchestration tool, initially developed by Google and later donated to CNCF (Cloud Native Computing Foundation). Container orchestration means Kubernetes will manage the lifecycle of the containers based on a desired state.
The name Kubernetes originates from Greek, meaning helmsman or captain.
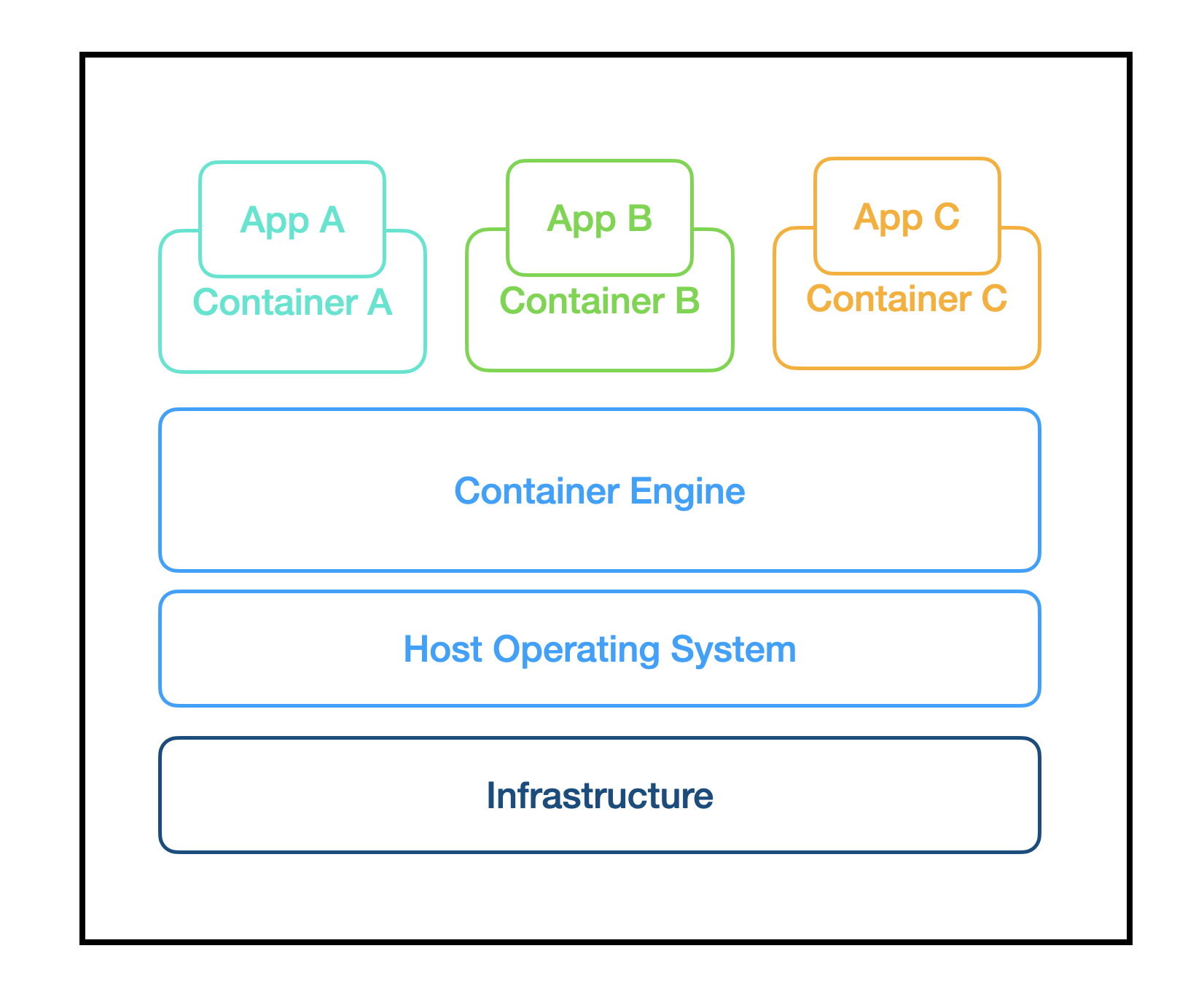
What is a Container ?
A container is a ready-to-run software that packages up code and all its dependencies so the application runs quickly and reliably regardless of the environment where it runs.
Application are decoupled from the underlying host architecture using containers. Multiple containers can run on the same machine as isolated processes.
Why use Kubernetes ?
Kubernetes improves the applications’s availability with this key features:
Automated rollouts and rollbacks:Supports of rollouts and rollbacks based on the desired state of the application.Horizontal Scaling:Kubernetes can scale up or scale down the application based on the needs.Self-Healing:It restarts containers that fail, replaces and reschedules containers when nodes die, kills containers that don’t respond to your defined health check.Storage Orchestration:Kubernetes abstract storage and automatically mount the storage system of your choice (local, cloud, NFS, etc…).Service Discovery and Load Balancing:No need to modify your application to use an unfamiliar service discovery mechanism. Kubernetes gives Pods their own IP addresses and a single DNS name for a set of Pods, and can load-balance across them.Designed for extensibility:Add features to your Kubernetes cluster without changing upstream source code.
Kubernetes Architecture
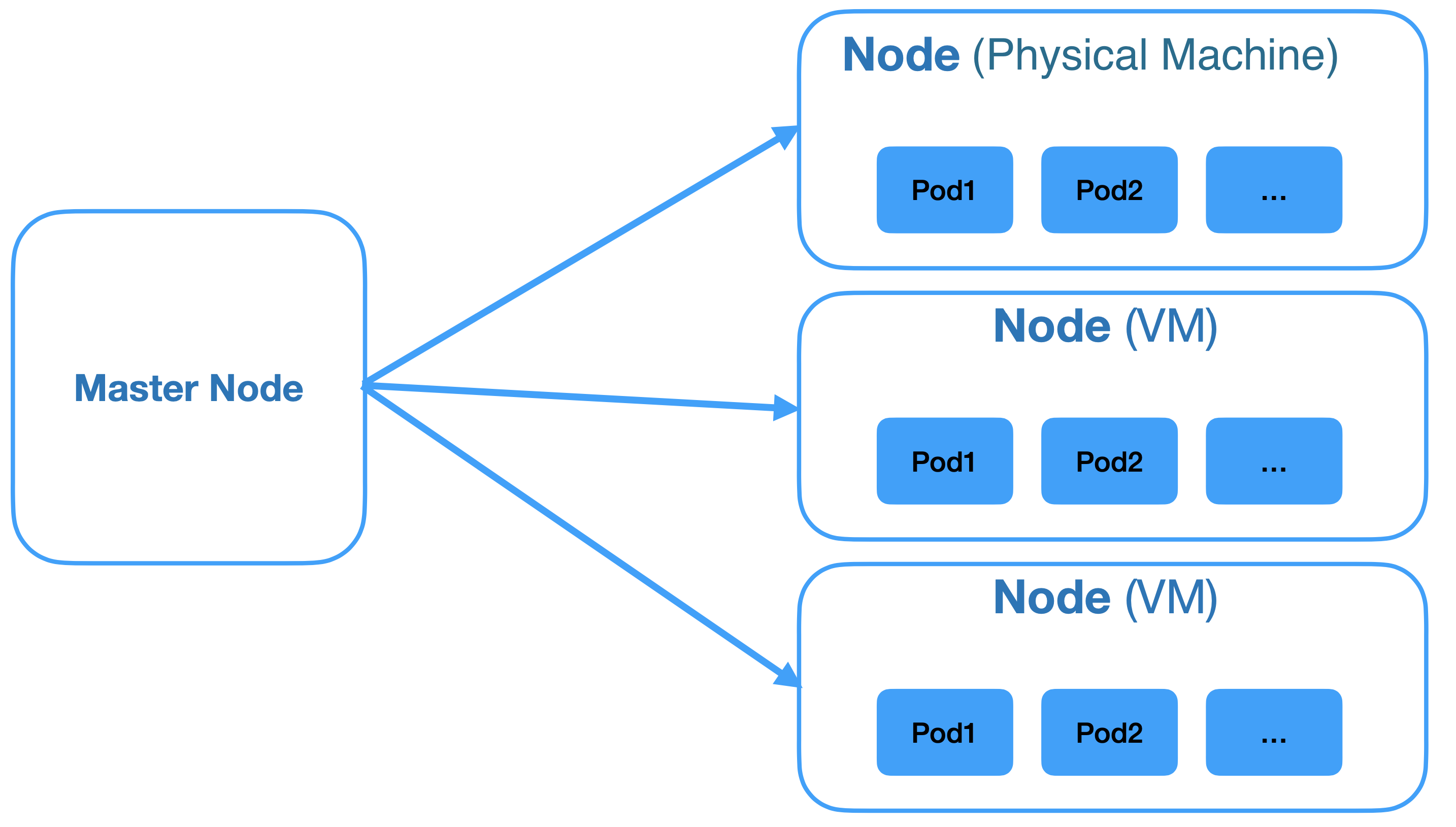
A Kubernetes cluster consist of a master node and one or more worker node. Node can be physical machine or virtual machine and a cluster can have nodes of mixed type.
The master node holds the control plane who is responsible of managing the worker node and the pods (a set of running containers).
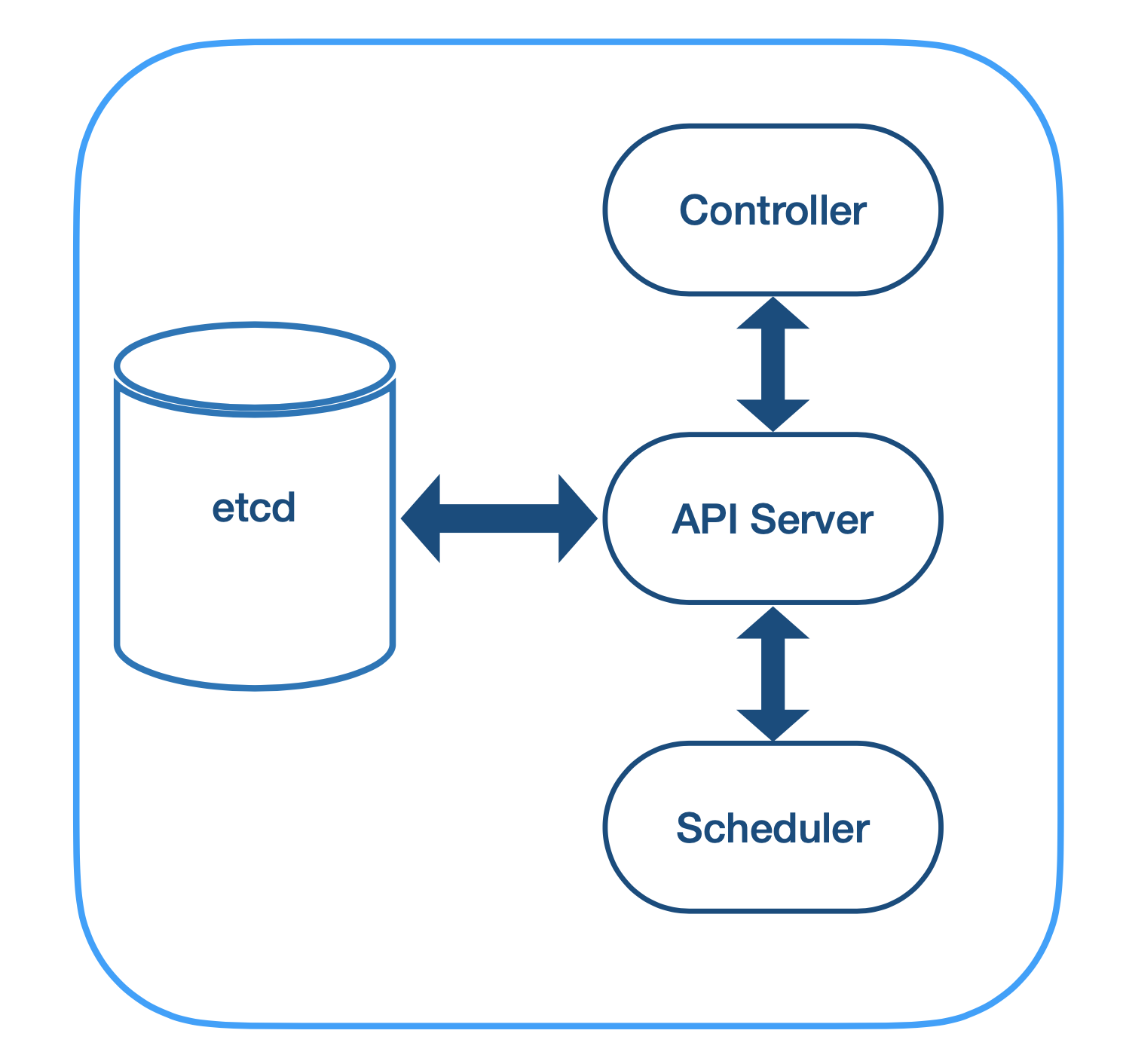
The control plane
The control plane contains several components as describe below
etcd: Is a distributed key-value store used to backup the cluster state at any point of time and also store configuration data.Controller Manager: A nonterminating loop that watch the state of the cluster through theAPI Serverand makes changes to meet the desired state.API Server: Is the entry point for the control plane through REST API call. It validates, configures and executes all the commands and store all change in theetcd.Scheduler: Using the resources available and also the requirements and constraints asked, the scheduler is responsible for placing pods and workload utilization.
The node components
The node components run on every worker node and are responsible to provide the Kubernetes runtime environment.
Kubelet: Kubelet agent communicates with the master node to get the pod specifications through theAPI serverand ensures that the containers described in those specs are running and healthy. If kubelet notices any issues, it will try to self healing by restarting the pod or recreate it on anotherworker node.Kube-Proxy: It is the core networking component inside the cluster, responsible for maintaining the network network rules on nodes. These network rules allow network communication to your Pods from network sessions inside or outside of your cluster.Container runtime: It is the software in charge of running containers.