Istio
I hope this series of blog posts will help people in their service mesh journey.
- What is a Service Mesh ?
- Istio
In this guide, we will install and test Istio.
Istio is an open source service mesh that layers transparently onto existing distributed applications.
Istio’s powerful features provide a uniform and more efficient way to secure, connect, and monitor services.
Perquisites
- A Kubernetes cluster running the version 1.22, 1.23, 1.24 or 1.25.
- Loadbalancer service (cloud lb, metallb)
Installation
All the guide was run on MacOS and used a Kubernetes cluster 1.24 provisioned with kubeadm.
Download istioctl.
> curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | sh -
> cd istio-X-YY-Z
> export PATH=$PWD/bin:$PATH
Run the precheck to ensure Istio can be installed (or upgraded) on your environment.
> istioctl experimental precheck
No issues found when checking the cluster. Istio is safe to install or upgrade!
To get started, check out https://istio.io/latest/docs/setup/getting-started/
Now it is time to install Istio.
We are using the demo profile that contains defaults values for testing purpose.
There is another profile production.
> istioctl install --set profile=demo -y
✔ Istio core installed
✔ Istiod installed
✔ Ingress gateways installed
✔ Egress gateways installed
✔ Installation complete
Making this installation the default for injection and validation.
Istio is now installed in the istio-system namespace.
> kubectl get po -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
istio-egressgateway-688d4797cd-4gjwr 1/1 Running 0 3m32s
istio-ingressgateway-6bd9cfd8-xz8b9 1/1 Running 0 3m32s
istiod-68fdb87f7-nnpp2 1/1 Running 0 3m42s
We can retrieve the external IP address of Istio by looking at the services.
I replace mine with X.X.X.X
> kubectl get svc -n istio-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
istio-egressgateway ClusterIP 10.109.214.225 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP 4m31s
istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.98.55.56 X.X.X.X 15021:30712/TCP,80:32215/TCP,443:31094/TCP,31400:31664/TCP,15443:32433/TCP 4m31s
istiod ClusterIP 10.111.57.100 <none> 15010/TCP,15012/TCP,443/TCP,15014/TCP 4m41s
Configuration
We will now create a namespace named demo and label it to instruct Istio to automatically inject Envoy sidecar proxies to any application we will deploy in that namespace.
> kubectl create ns demo
> kubectl label namespace demo istio-injection=enabled
We can verify it by running:
> kubectl get ns demo --show-labels
Deploy demo application
It’s time to deploy the sample app bookinfo provide by Istio.
Ensure we are in the istio directory and apply the manifest.
> kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml -n demo
service/details created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-details created
deployment.apps/details-v1 created
service/ratings created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-ratings created
deployment.apps/ratings-v1 created
service/reviews created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-reviews created
deployment.apps/reviews-v1 created
deployment.apps/reviews-v2 created
deployment.apps/reviews-v3 created
service/productpage created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-productpage created
deployment.apps/productpage-v1 created
We can check all the pods are up and running.
kubectl get po -n demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
details-v1-7d4d9d5fcb-bwrxx 2/2 Running 0 89s
productpage-v1-66756cddfd-2ffqh 2/2 Running 0 88s
ratings-v1-85cc46b6d4-t4r6m 2/2 Running 0 89s
reviews-v1-777df99c6d-f5blv 2/2 Running 0 89s
reviews-v2-cdd8fb88b-d4dxz 2/2 Running 0 89s
reviews-v3-58b6479b-shbvn 2/2 Running 0 89s
To verify that everything works properly, let’s deploy a pod containing curl binary and ensure that we can connect to the application.
By looking at the service, we can see the app is listening on port 9080.
First apply the pod manifest.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: curl
labels:
app: curl
spec:
containers:
- command:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- --
args:
- while true; do sleep 30; done;
image: curlimages/curl
name: curl
Then try to curl the product page productpage:9080
> kubectl exec curl -- curl -Ss productpage:9080
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
<meta charset="utf-8"
...
...
...
Expose the app to outside
To be able to access our application from the outside, we need to create an t
Istio Ingress Gateway manage inbound and outbound traffic for your mesh.
We configure the host and port available for requests.
Let’s apply the Gateway and VirtualService provide in the sample.
It looks like:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway # use istio default controller
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: bookinfo
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- bookinfo-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
exact: /productpage
- uri:
prefix: /static
- uri:
exact: /login
- uri:
exact: /logout
- uri:
prefix: /api/v1/products
route:
- destination:
host: productpage
port:
number: 9080
> kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml -n demo
gateway.networking.istio.io/bookinfo-gateway created
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/bookinfo created
We can validate the configuration with istioctl
> istioctl analyze -n demo
✔ No validation issues found when analyzing namespace: demo.
We need to retrieve the External IP of the istio-ingressgateway:
> kubectl get svc -n istio-system
With the IP, we can now ensure the external access, just by running curl command:
> curl http://[External-IP]:80/productpage
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
...
...
...
Observability
One of the key features of service mesh is observability.
Istio provide basic installation for the following observability tools:
let’s install them.
> kubectl apply -f samples/addons
We will not go into details of each tool but more have an overview of what can be achieve for observability.
Jaeger
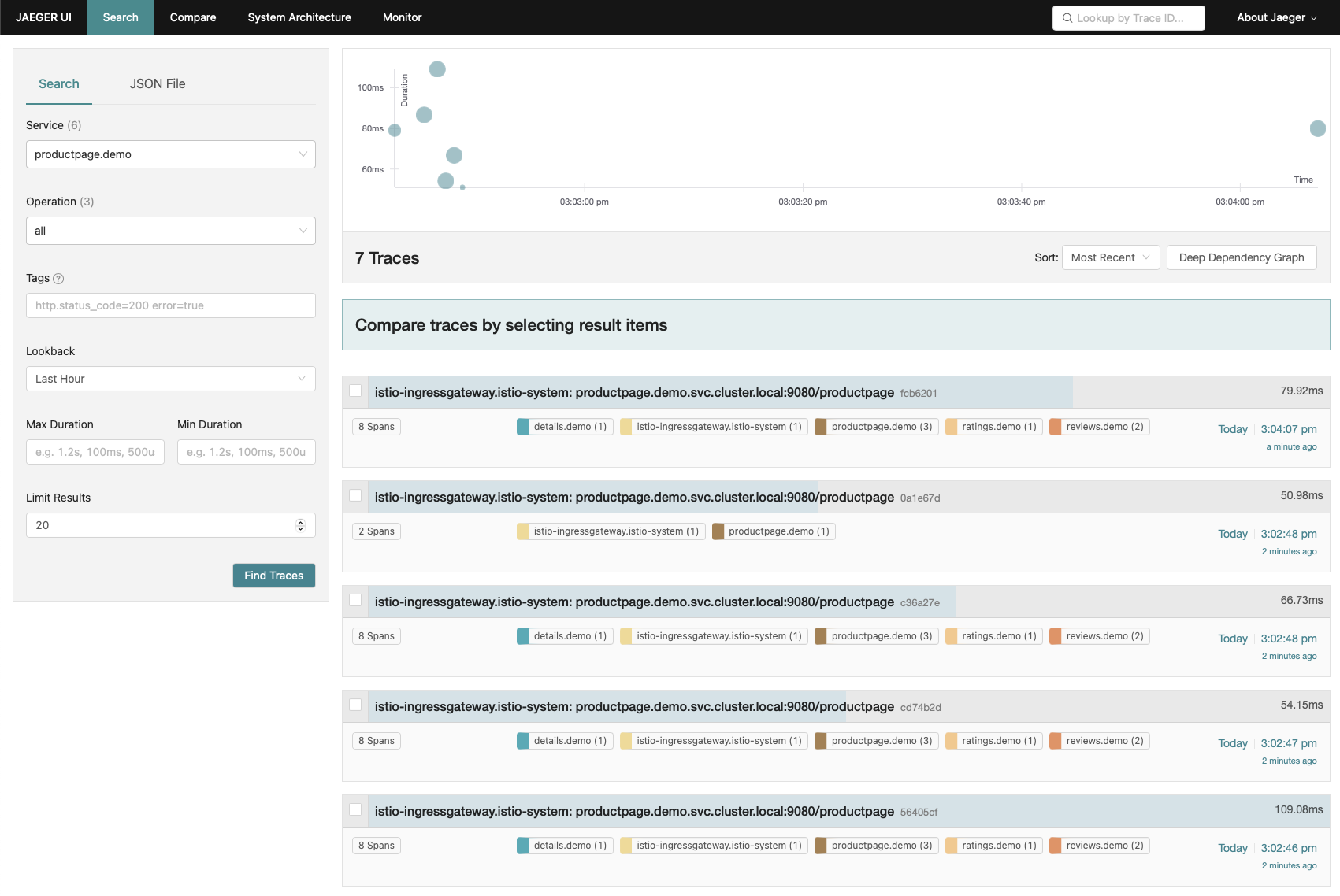
Jaeger is a distributed tracing tool that allows to trace application regardless of the language or framework used.
Before being able to see anything we need to generate some trace by accessing our application one or more time.
> curl http://[External-IP]:80/productpage
Now, we can launch the jaeger dashboard to see the traces generated.
> istioctl dashboard jaeger
http://localhost:16686
Grafana
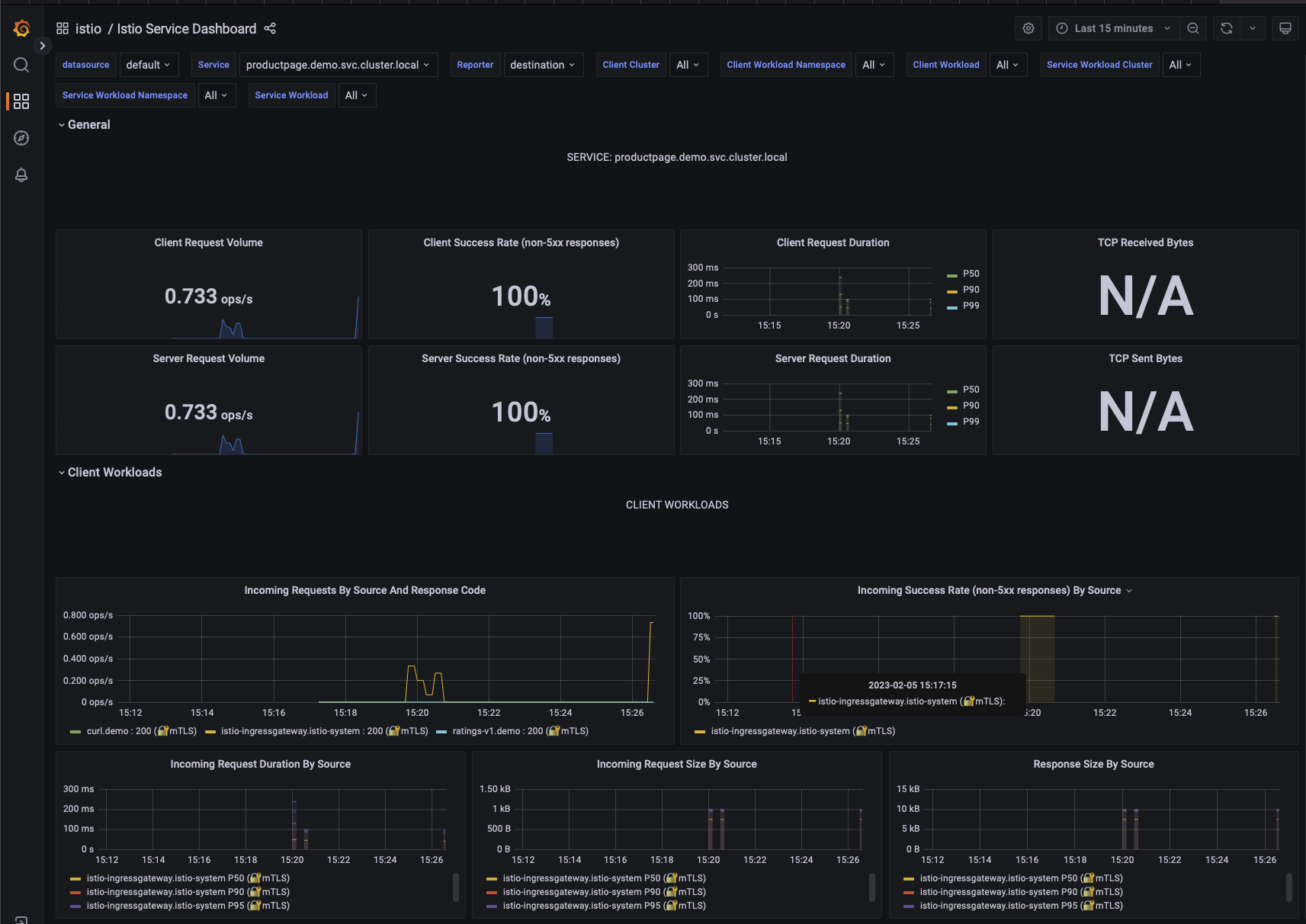
Grafana is an open source monitoring solution with an amazing community that provide all sort of ready to use dashboards.
Of course it’s possible to build are own as well.
> istioctl dashboard grafana
http://localhost:3000
On Grafana, we need to go to the dashboard menu and then inside the istio folder.
Let’s open the Istio Service Dashboard and select the productpage’s service.
Kiali
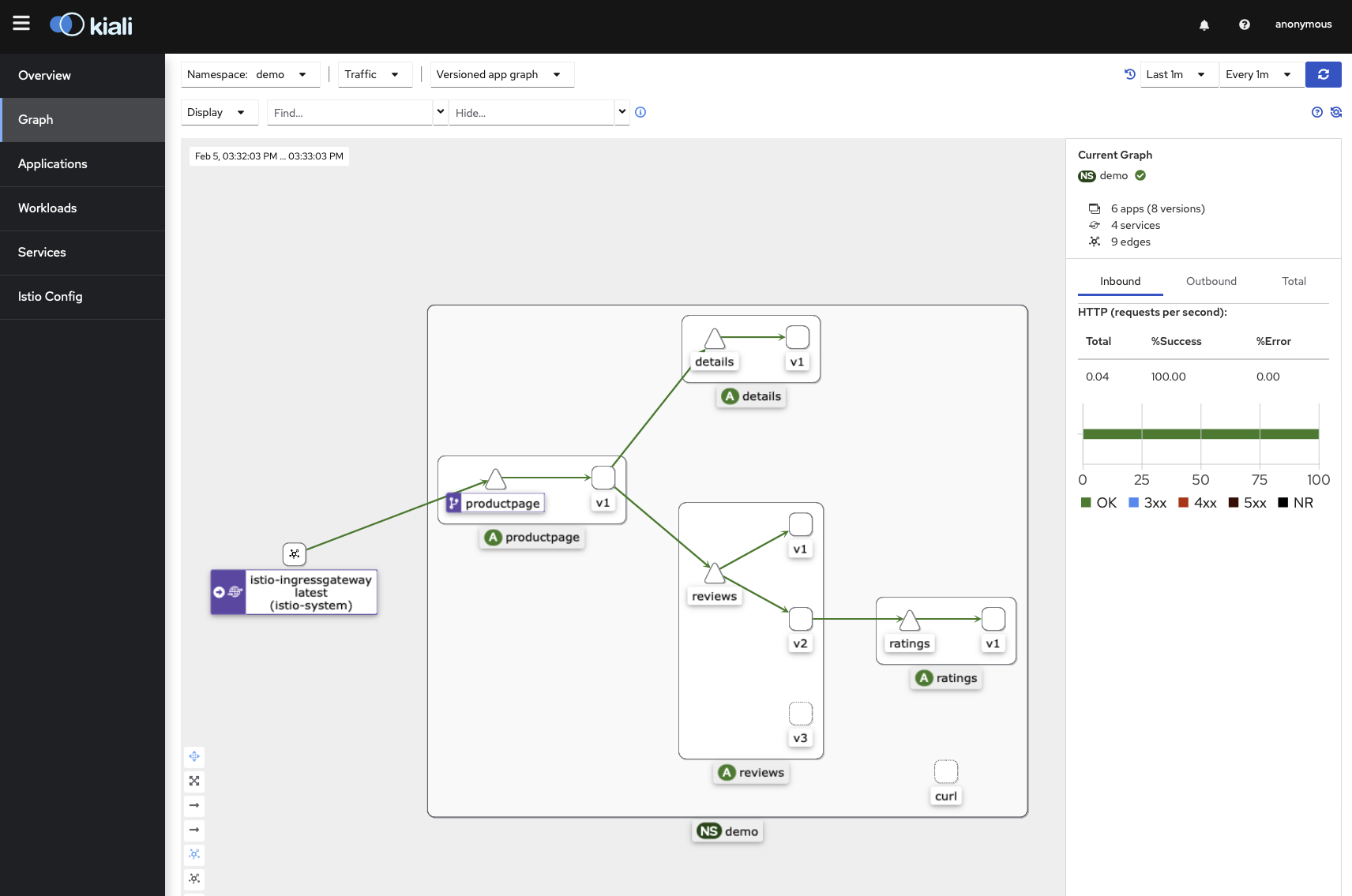
Kiali is an open source solution to observe microservices traffic flows inside a service mesh.
Let’s generate some traffic again and start the Kiali dashboard.
> curl http://[External-IP]:80/productpage
> istioctl dashboard kiali
http://localhost:20001/kiali
We need to go to the Graph menu and select our demo namespace in the dropdown list.
We can see the relationships between the service of the app and visualize the its traffic flow.
Cleaning up
> kubectl delete -f samples/addons
> istioctl uninstall --purge
> kubectl delete ns istio-system
> kubectl delete -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml -n demo
Conclusion
Thanks to all resources provided by Istio, we are able to setup very quickly a demo of service mesh and experienced with it.